Executive Summary
As of October 2015, twenty-two states and the District of Columbia expressly prohibited employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation. Of those states, nineteen and the District of Columbia also expressly prohibited discrimination on the basis of gender identity. This report measures how frequently these laws are used by LGBT people, compared to how frequently race non-discrimination laws are used by people of color, and sex non-discrimination laws are used by women.
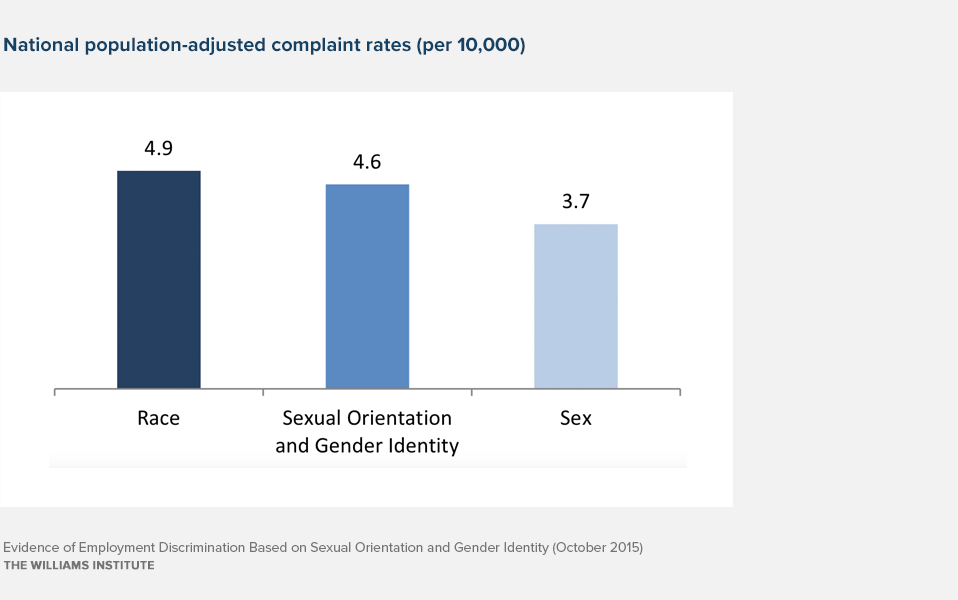
An aggregation of all available state-level data shows that sexual orientation and gender identity employment non-discrimination laws are used by LGBT people at a similar rate to the use of race non-discrimination laws by people of color and sex discrimination laws by women. Nationally, on average, approximately 4.6 complaints of sexual orientation and gender identity discrimination are filed for every 10,000 LGBT workers each year, compared to approximately 4.9 complaints of race discrimination filed for every 10,000 workers of color, and 3.7 complaints of sex discrimination filed for every 10,000 female workers.
The findings refute the argument that discrimination against LGBT people does not occur often enough to establish a need for protective laws. Additionally, even with similar filing rates, sexual orientation and gender identity complaints will not overwhelm government agencies because the absolute number of such complaints filed is low. The annual average number of sexual orientation and gender identity complaints for all 14 states that provided data was 1,600, compared to 9,800 complaints of race discrimination and 13,700 complaints of sex discrimination.
Download the full report